
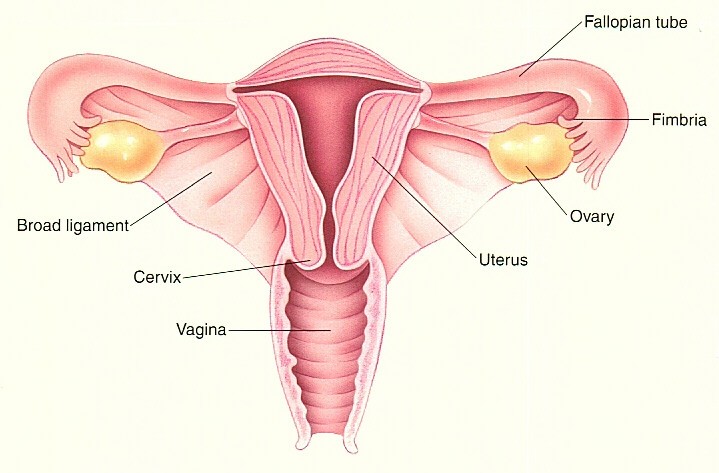
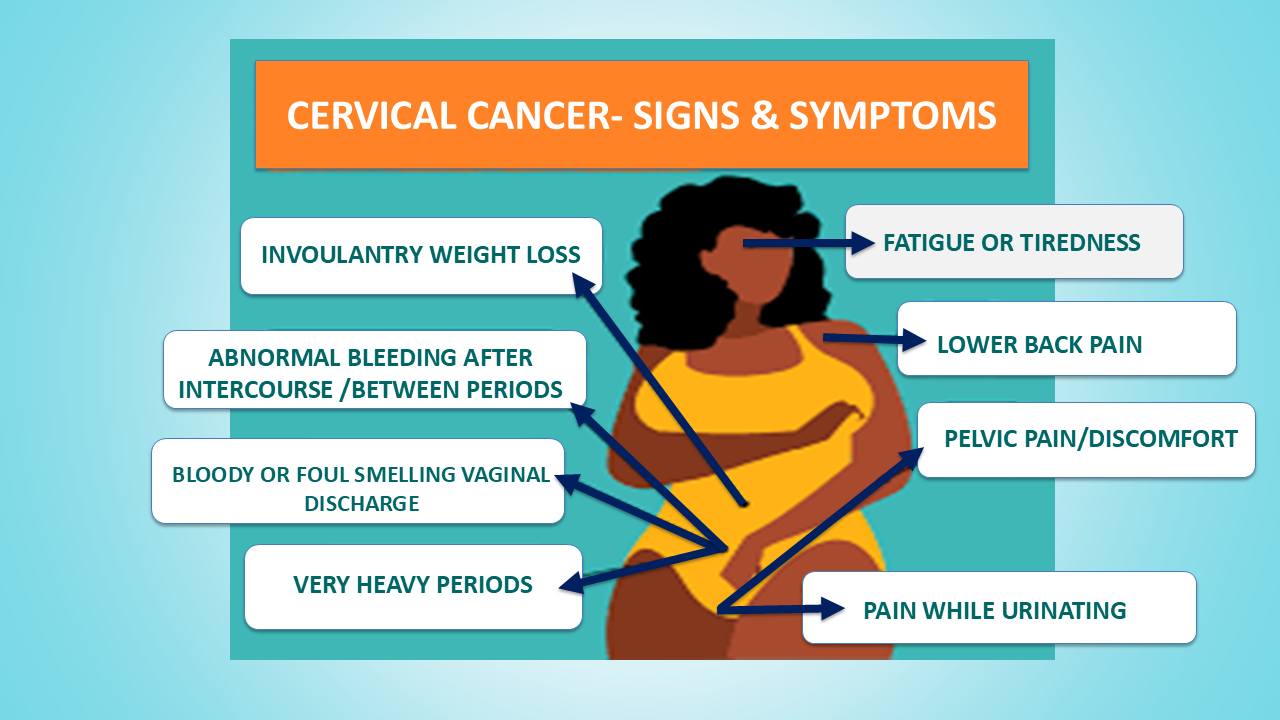
-> Cervical cancer occurs in the cells of the cervix, the lower part of the uterus. In India, 200 women die each day due to cervical cancer.
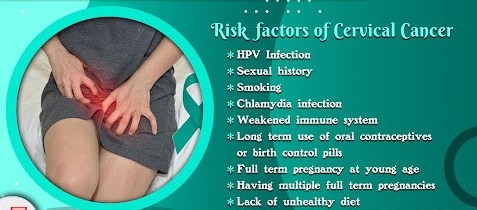
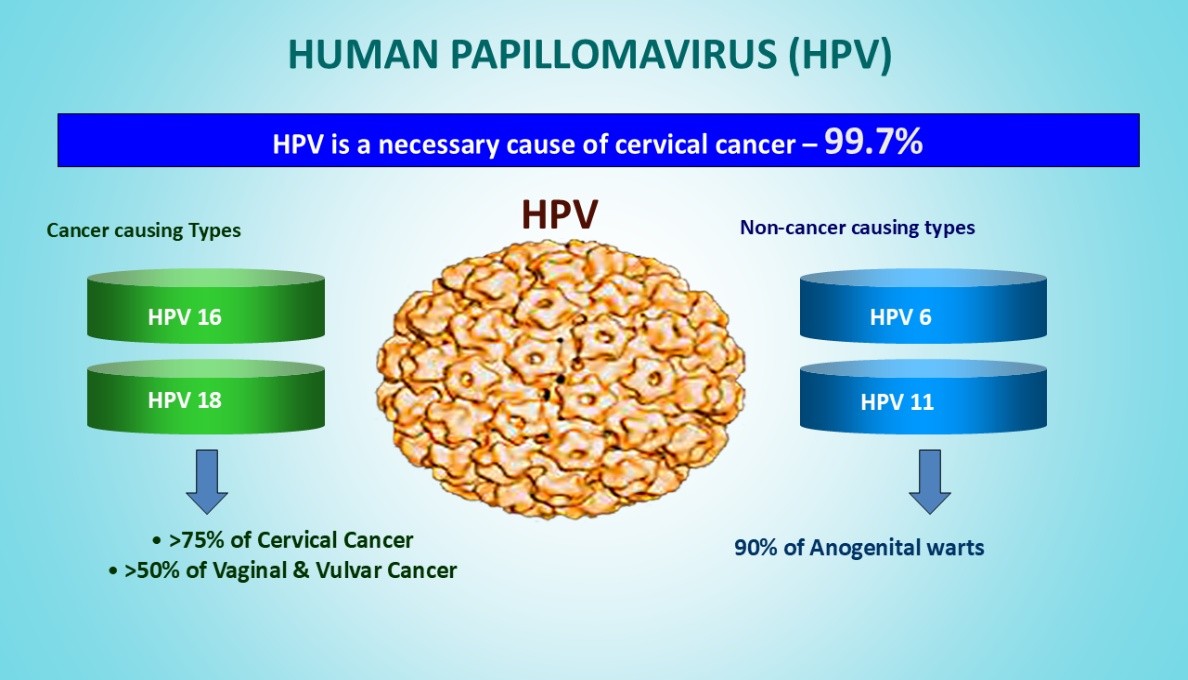
-> It is primarily caused by persistent infection with high-risk types of HPV.
-> Early detection and vaccination can prevent most cases.
-> HPV is transmitted through sexual contact.
-> A person with HPV can pass the infection even without symptoms.
-> Skin-to-skin contact other than sexual activity
-> HPV can be transmitted through fingers or contaminated surfaces
-> Warts can spread infection if touched and hands are not washed
-> Through amniotic fluid, placenta, or during natural birth
-> HPV can be passed from a birthing person to their baby
HPV is one of the most prevalent sexually transmitted infections. Vaccines induce stronger immunity than natural infection. It is found that 8 in 10 women may contract HPV at some point in their lives.
-> Pap Smear: Detects precancerous or cancerous cells
-> HPV Test: Identifies high-risk HPV types
-> Colposcopy: Further examination if abnormalities are found
-> Women 21–29: Pap Smear every 3 years
-> Women 30–65: Pap Smear + HPV Test every 5 years
-> HPV Vaccination (e.g., Cervavac, Gardasil)
-> Regular Screening (Pap Smear, HPV Test)
-> Safe sexual practices
-> Smoking cessation
-> Cervavac: India’s indigenous, cost-effective vaccine
-> Gardasil & Gardasil 9: Protect against HPV types 6, 11, 16, 18
-> Affordable & accessible
-> Strong immunity against high-risk HPV
-> Suitable for girls & women aged 9–26
FOR GIRLS 9–14 YEARS
-> Two doses
-> First – (as elected date)
-> Second – (6 months of first dose)
FOR GIRLS 15–26 YEARS
-> Three doses
-> First – (as elected date)
-> Second – (2 months of first dose)
-> Third – (6 months)
-> Myth: HPV vaccines promote sexual activity.
-> Reality: They only protect against cancer-causing HPV strains.
-> Myth: Only sexually active women need the vaccine.
-> Reality: Most effective before HPV exposure.
-> Myth: Vaccines are unsafe.
-> Reality: Rigorously tested and proven safe.

-> Prevents most cases of cervical cancer
-> Reduces healthcare costs
-> Provides long-term immunity
-> Pain at injection site
-> Fever or fatigue
-> Dizziness or nausea (rare)